Habitable Zone Exoplanets
Exploring potentially habitable worlds beyond our solar system
About This Project
This website presents an analysis of exoplanets located in the habitable zone of their host stars, based on data from the Open Exoplanet Catalogue.
The habitable zone is the region around a star where conditions might be suitable for liquid water to exist on a planet's surface - a key ingredient for life as we know it. The boundaries used in this analysis are based on the conservative habitable zone boundaries from Kopparapu et al. (2013):
- Inner edge: Recent Venus (0.75 AU for Sun-like star)
- Outer edge: Early Mars (1.77 AU for Sun-like star)
These boundaries are scaled based on the star's luminosity for stars of different types.
Summary Statistics
211
Total planets in habitable zone
13
Earth-like planets
(0.1-2 Earth masses)
31
Super-Earths
(2-10 Earth masses)
17/150
Neptune-like / Gas Giants
Mass range: 0.11 to 5636.94 Earth masses
Visualizations
Habitable Zone Exoplanets: Mass vs. Orbital Distance
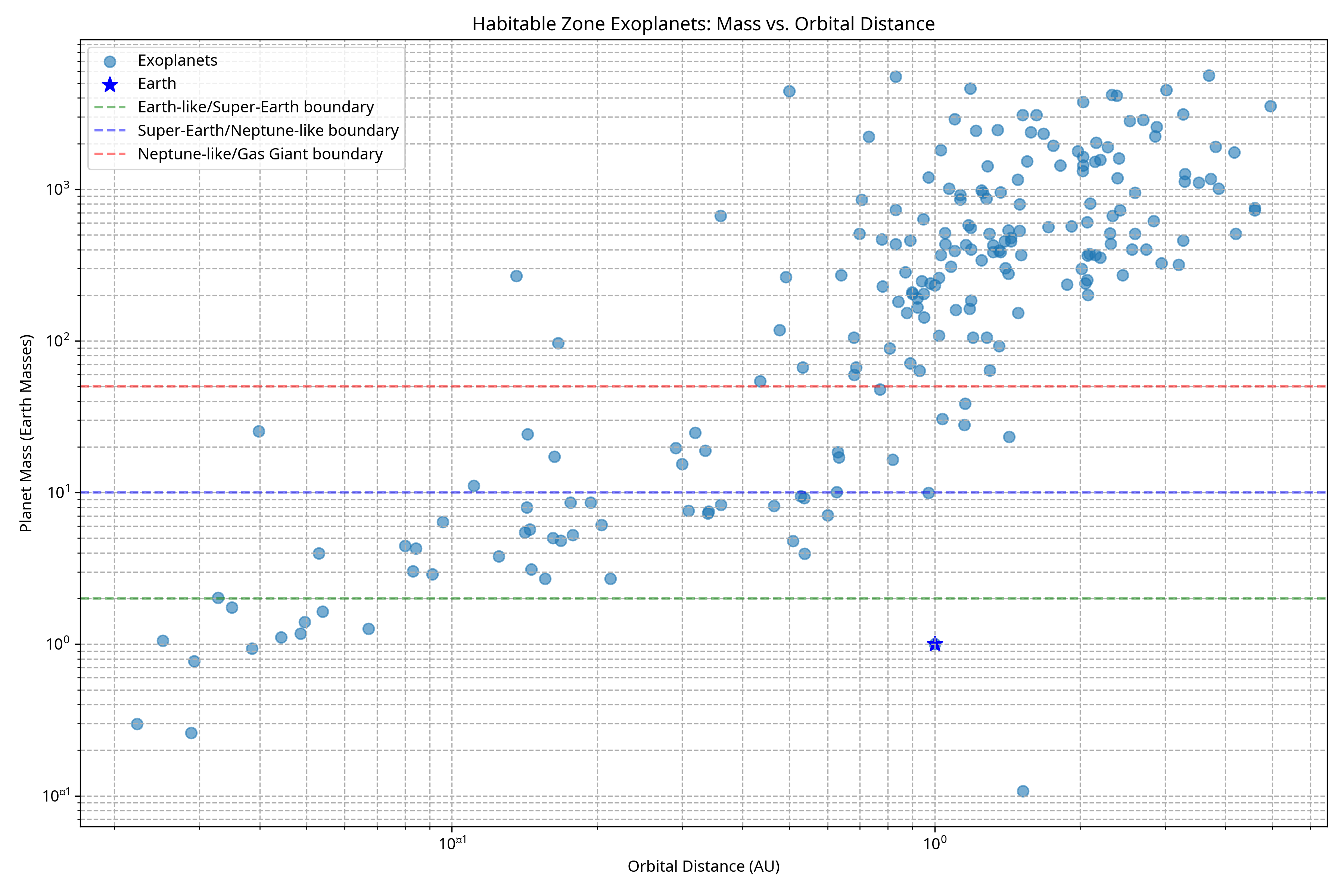
This logarithmic plot shows the relationship between planet mass (in Earth masses) and orbital distance (in AU). Horizontal lines indicate the boundaries between different planet categories.
Distribution of Habitable Zone Planets by Mass (< 100 Earth Masses)
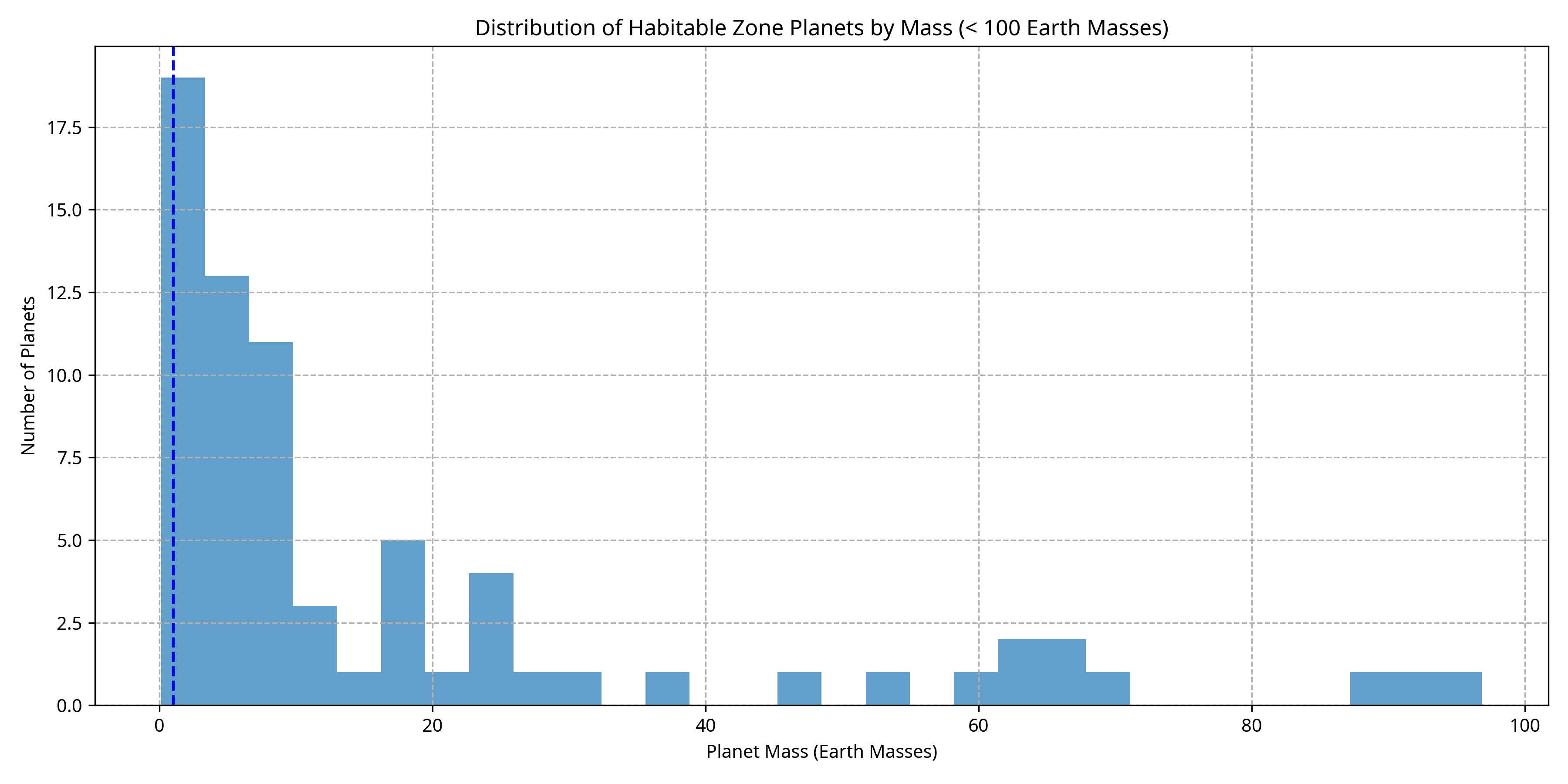
This histogram shows the distribution of planet masses for planets less than 100 Earth masses. The vertical blue line indicates Earth's mass for reference.
Habitable Zone Planets Sorted by Mass
| Planet Name | Earth Masses | Orbit (AU) | HZ Inner (AU) | HZ Outer (AU) | Star |
|---|